Jeremiah Roe is a Synack Solutions Architect for the Federal and DoD space and We’re In! Podcast host. As a solutions architect, he helps organizations understand and implement effective security from an offensive perspective. He has an extensive background including work in the Marine Corps, network penetration testing, red team operations, wargaming and threat modeling.
What is interesting about you? Nothing, you say? Well, I beg to differ. There are many interesting things about you! Where do you work? What is your role at work? What are your interests? What are your hobbies? Where do you frequently go? And, how can this information be used against you by someone with malicious intent?
If you’re like me, you’ve always been intrigued by a good spy story: the how, the why, the operations, the tradecraft, the methodology. As a boy, I was always excited by the spy image. I would hang on every action scene depicted in movies and shows—I was enthralled by the bait and hook within the spy narrative.
Before we get into how your personal information and spies relate, let’s review some important definitions:
- Reconnaissance: “A preliminary survey to gain information, especially an exploratory military survey of enemy territory” – Merriam Webster
- Open-source intelligence (OSINT): “the collection and analysis of data gathered from open sources (overt and publicly available sources) to produce actionable intelligence.” – Wikipedia
- Social Engineering: “(in the context of information security) the use of deception to manipulate individuals into divulging confidential or personal information that may be used for fraudulent purposes.” – Google
- Spy: “A person who secretly collects and reports information on the activities, movements, and plans of an enemy or competitor.” – Google
Reading through these, we can see some parallels to cybersecurity beginning to take shape. If we alter a few words from what a definition of a spy is, we can easily see how a hacker could be synonymized with a spy.

Shifting this context changes perspectives on who could be considered to be malicious or a bad actor. The spy in your life could be a coworker, a friend, a neighbor, a family member, the person delivering your mail, the person sitting next to you on a plane. At this point, probabilities come in, context takes over and you realize your mother-in-law probably isn’t a covert operator hacking their way into your bank account (maybe).
Given that a malicious entity could be anyone at this point, where does that leave you?
As you begin to sift through the news you’ll begin seeing story after story about corporate espionage, insider threat, trade secrets stolen and malicious actors. Would you be able to tell if someone was an insider threat? How would you detect them? How would you protect your systems from being breached by them? Here are some recent headlines:
- FBI investigation determined Chinese-made Huawei equipment could disrupt US nuclear arsenal communications
- Ex-C.I.A. Engineer Convicted in Biggest Theft Ever of Agency Secrets
- Former Army Special Forces Officer Charged in Russian Espionage Conspiracy
In any offensive operation, the first phase is reconnaissance—digital attackers do the same thing. They want to know what’s there, what’s vulnerable, what’s end of life, what’s not properly maintained, what technologies are in use, what’s fully exposed and how they can coordinate an attack against you. Unfortunately, we often find that organizations aren’t taking the right steps to ensure their environments are properly secured. As for the reasons, I’ll let you pick.

To cultivate additional insight into your networks, here are some tools that offensive practitioners use to understand a network and its potential weak points.
|
|
Here’s a sample of the data some of these tools provide:
This first view is from a relational graph created by SpiderFoot in an actual operation we were conducting reconnaissance for. This is helpful in understanding how things connect to other things, which an attacker may exploit to try to find an avenue in.
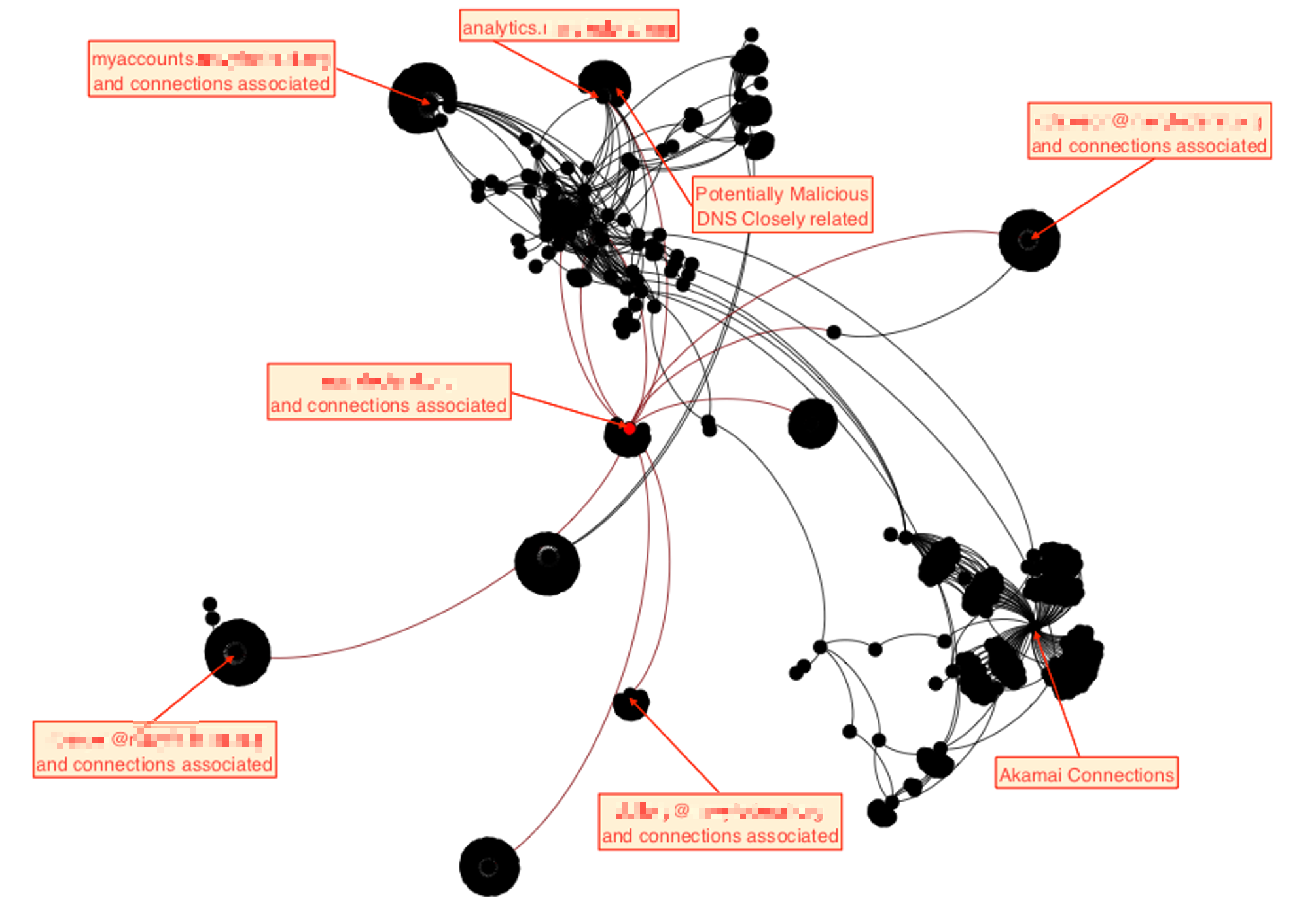
This next capture is from a tool called Recon-NG. It’s good to utilize in conjunction with other tools for identifying systems to target within an organization.
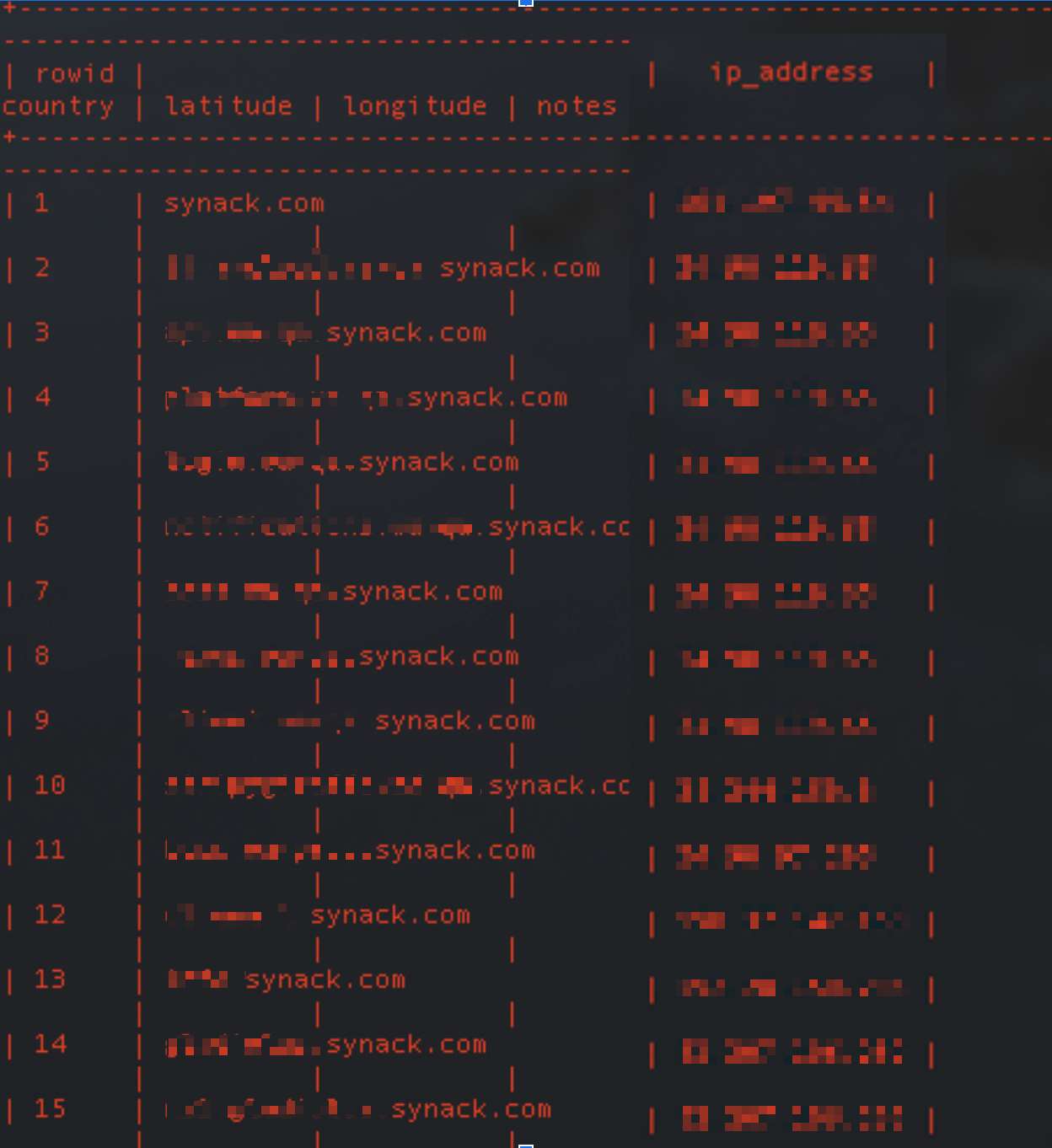
Recon-NG is a great tool for obtaining additional information about a target domain. It’s a command-line tool that can be ran on many Linux distributions that helps to contextualize data.
This is a fantastic tool for finding insight into people, places, interests, likes, location and potential social engineering avenues into an organization.
LinkedIn and other social media are rich sources of data for people looking for personal information to use in an attack.
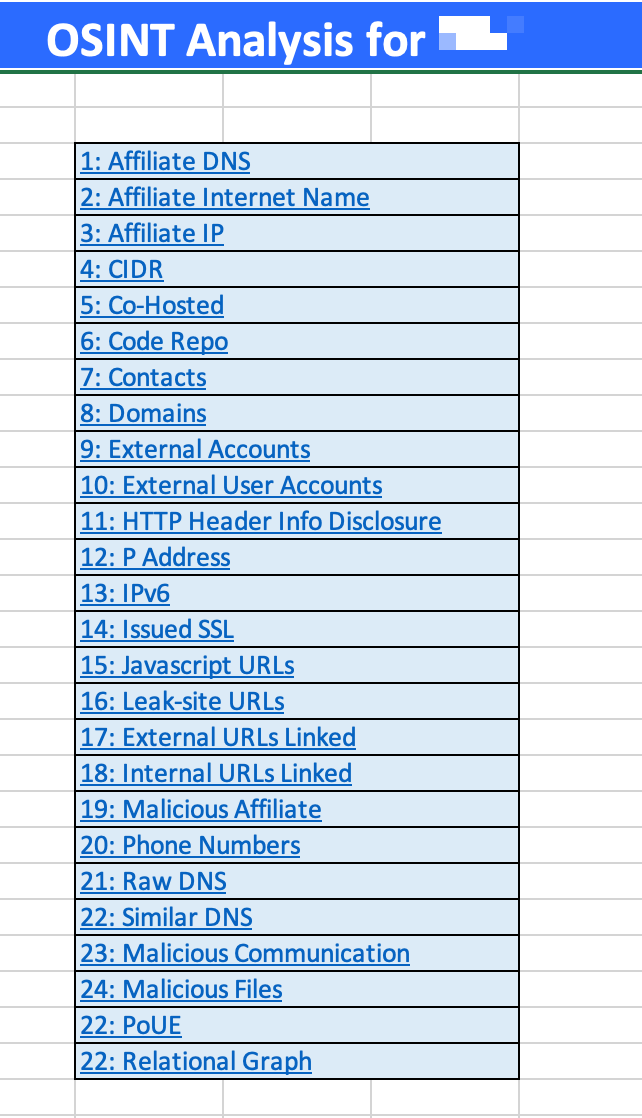
In developing an understanding of where your risks are within the organization, these are the types in information categories an attacker is looking for as well. Here’s a list of the types of information we were able to obtain in a real operation by utilizing Open Source Intelligence (OSINT) techniques:
Once an attacker compiles the data they’ve obtained, either internal or external, they can begin to craft an appropriate weaponization and delivery process that’ll have the highest chances of being successful. It’s often as easy as scraping the header information towards assets you’ve sent requests to. In the screenshot below, we highlight several responses that share versioning information that can be used in weaponizing an attack.

DATA = INTELLIGENCE
As you begin to dig into the weak points of an environment and its people, you begin to develop a level of insight into what their proclivities are. This is helpful in leveraging social engineering and phishing techniques which can also lead to a direct compromise. The most vulnerable (and easily exploitable) asset in any environment is always YOU!
At the end of the day, it’s the goal of the attacker to gain a foothold into your environment through any means necessary, whether they can leverage a remote capacity or need to have some sort of physical presence. If they want to get in, they can usually find a way in. By increasing the attacker’s cost to compromise, you will reduce the overall risk of an attack taking place. If there’s anything a spy (or hacker) hates, it’s being found out and identified. Take the steps I’ve listed here and look at your network with a spy’s perspective to find the best ways to harden your security posture.
Want to hear more from Jeremiah? Check out his episode on Darknet Diaries.




